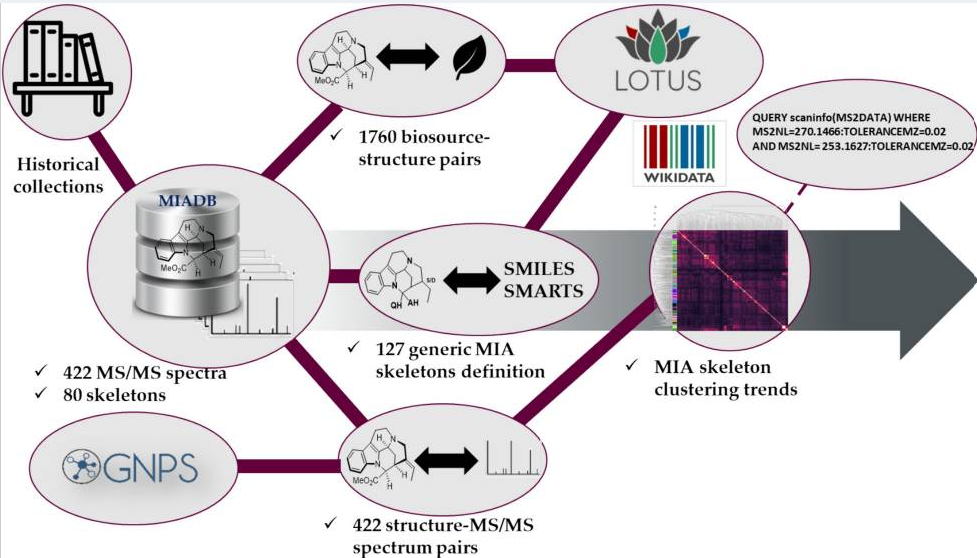
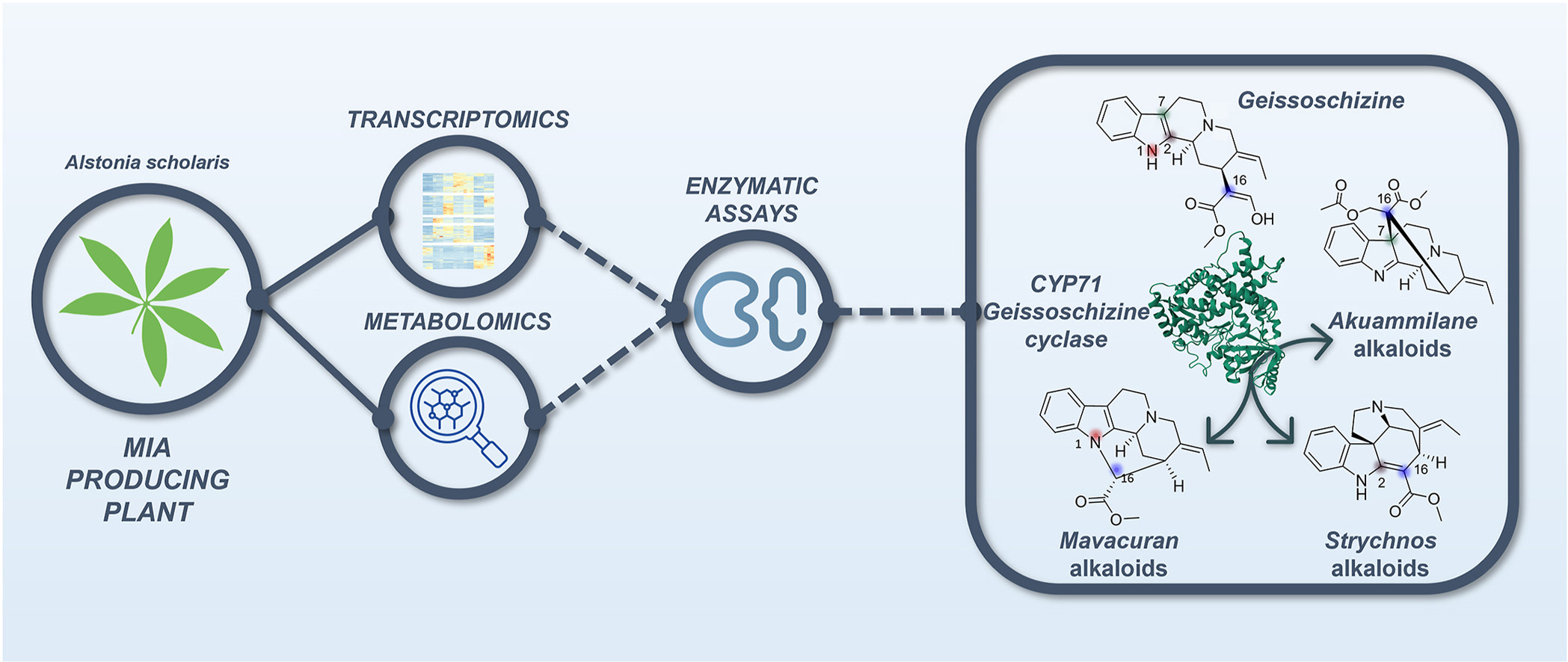
Plants biosynthesize a broad range of natural products through specialized and species-specific metabolic pathways that are fuelled by core metabolism, together forming a metabolic network. Specialized metabolites have important roles in development and adaptation to external cues, and they also have invaluable pharmacological properties. A growing body of evidence has highlighted the impact of translational, transcriptional, epigenetic and chromatin-based regulation and evolution of specialized metabolism genes and metabolic networks. Here we review the forefront of this research field and extrapolate to medicinal plants that synthetize rare molecules. We also discuss how this new knowledge could help in improving strategies to produce useful plant-derived pharmaceuticals.