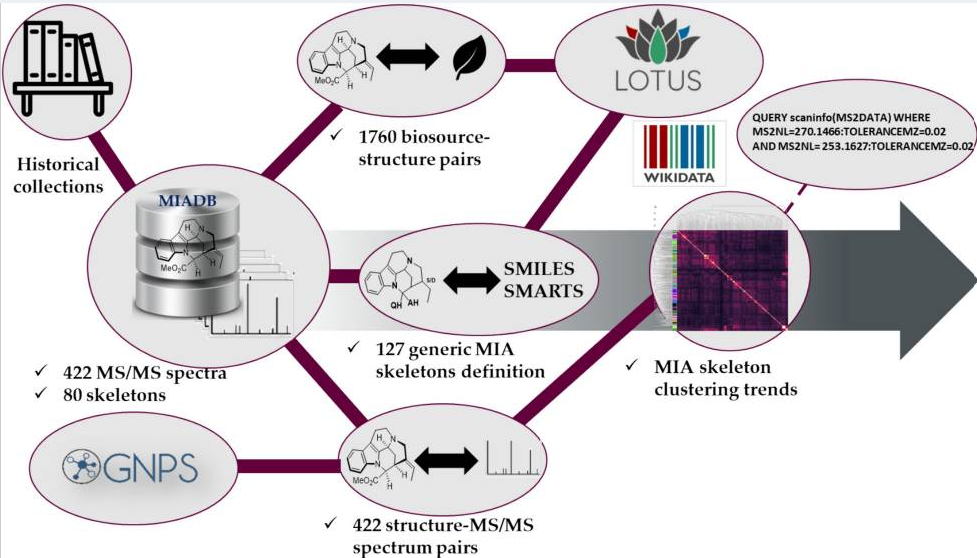
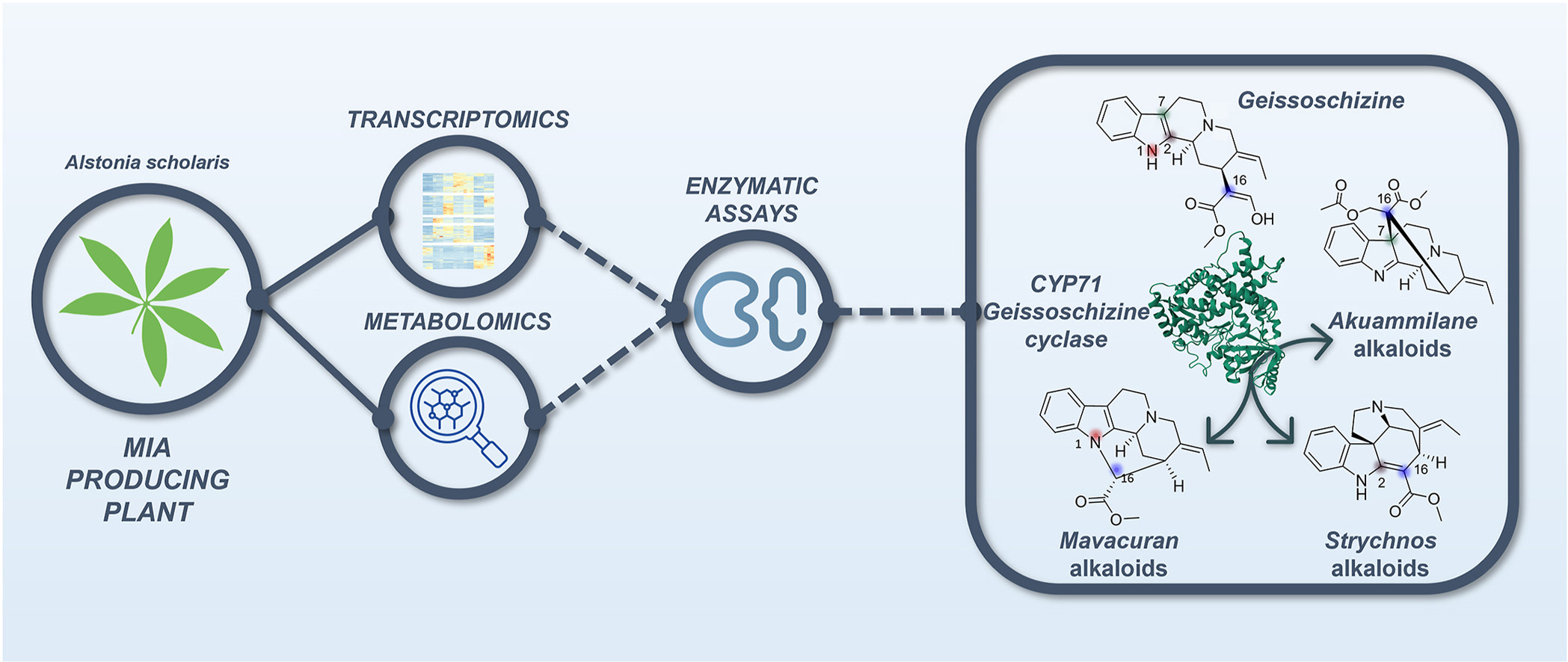
Chemical investigation of the emblematic Catharanthus roseus led to the discovery of trirosaline (1), the first example of a tris-ajmalicine-type monoterpene indole alkaloid and the first natural trimeric MIA ever reported from this deeply dug plant species. Its structure was primarily elucidated based on NMR and HRESIMS analyses, and the nature of its unique intermonomeric linkages was firmly confirmed based on a combination of empirical computation and ML-J-DP4 study. Its absolute configuration was mitigated by comparison of experimental and TDDFT-simulated electronic circular dichroism (ECD) spectra. A possible biosynthetic pathway for trirosaline (1) was postulated.